
In this case, the Nitrogen atom forms three covalent bonds with the set of surrounding Chlorine atoms. ‘X’ represents the number of atoms bonded to the central atom. ‘A’ here represents the central Nitrogen atom.
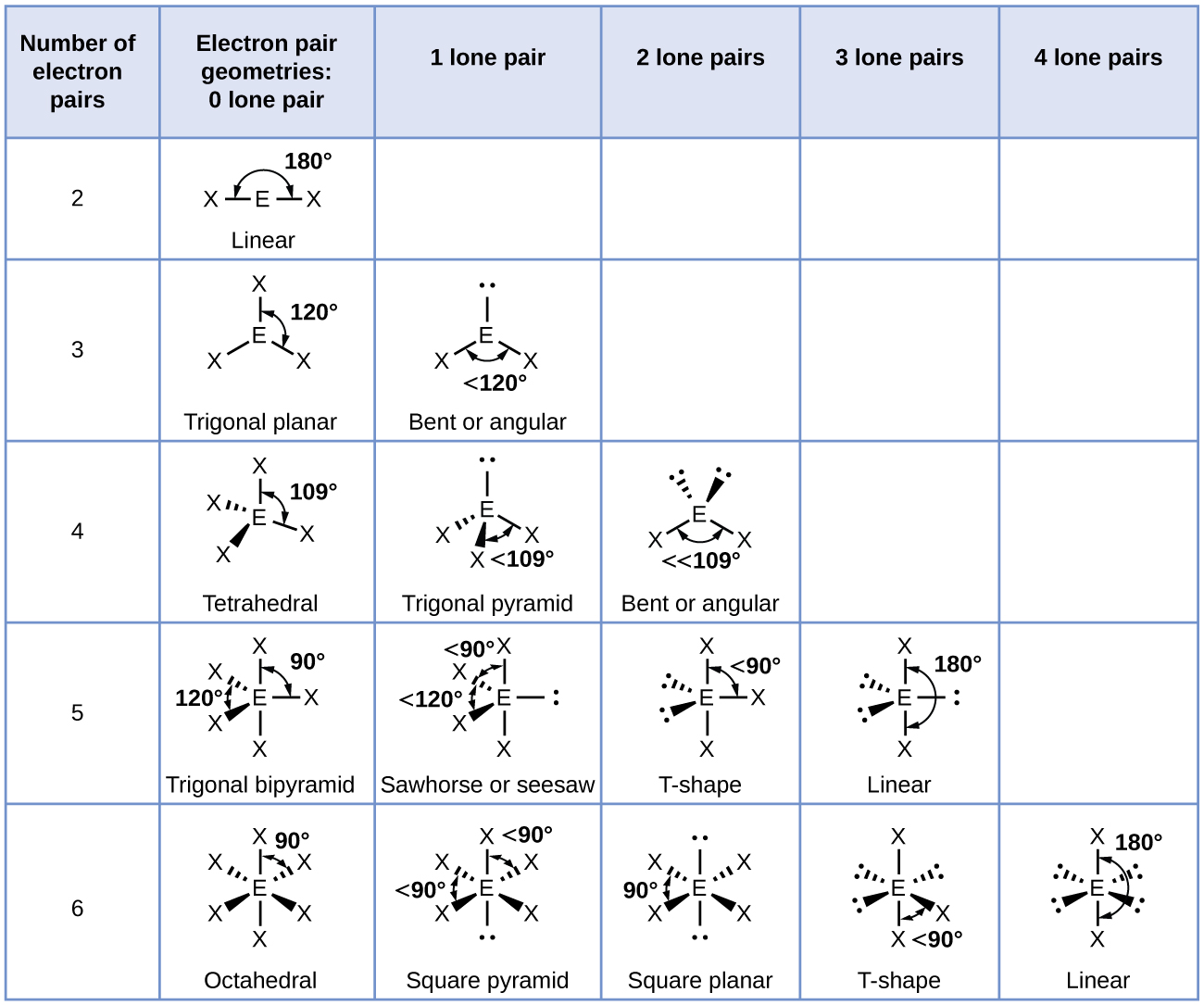
We can use the A-X-N method to confirm this. The figures above help visualize the change in molecular geometry due to repulsion from the lone pair on Nitrogen. However, the lone pair attached to the Nitrogen atom repels the Chlorine atoms to give a Trigonal Pyramidal structure. The presence of three Chlorine atoms presents a Trigonal Planar shape. This repulsion pushes the atoms apart to give molecular geometry. From the Lewis structure, it can be observed that Nitrogen is the central atom while the set of Chlorine atoms present in the molecule surround the Nitrogen atom.Īccording to the VSEPR theory, electron regions on atoms will repel each other as much as possible. The Lewis structure of a compound gives insight into its molecular geometry and shape. According to the VSEPR theory (Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory), the lone pair on the Nitrogen atom will repel the atoms around it, pushing it down it further, resulting in bond angles of 107.1°. The bond angles, in this case, are expected to be 109.5°. However, the presence of a lone pair changes the shape into a Trigonal Pyramidal one. There are three Chlorine atoms surrounding the central Nitrogen atoms. Therefore, the Nitrogen atom at the center of Trichloramine has an sp 3 hybridization. This gives the Nitrogen atom a steric number of 4, i.e., there are four domains attached to it. There is also a lone pair attached to the Nitrogen atom. In this case, the Nitrogen atom in Trichloramine forms three sigma bonds with the surrounding Chlorine atoms. The bond between atoms (covalent bonds) and Lone pairs count as electron domains. An easy way to determine the hybridization of an atom is to calculate the number of electron domains present near it. The Hybrid orbitals formed to give a more accurate description of electron regions while also resulting in more stable bonds. Molecular structure and bond formation can be better explained with hybridization in mind. The set of Chlorine atoms surrounds the central Nitrogen atom. Nitrogen is the least electronegative atom in the group and, therefore, takes its place as the central atom. Next, we form a skeletal structure by determining the central atom(s). Twenty-six valence electrons are available as building blocks for the Lewis structure. Therefore, the total number of valence electrons present in Trichloramine(NCl 3) is given by:ĥ + 21 = 26 valence electrons Lewis Structure Assembly Therefore, the three Chlorine atoms present contribute 7 x 3 = 21 valence electrons. The possibility of electrons in its d shell makes it hypervalent. Chlorine’s electronic configuration is given by 3s 23p 5. Therefore, the lone Nitrogen atom in NCl 3 contributes 5 x 1 = 5 valence electrons.īeing in group 7 of the periodic table, chlorine has seven valence electrons. Nitrogen is in group 5 of the periodic table with the electronic configuration 1s 22s 22p 3.

Let us determine the number of valence electrons present in this molecule. Trichloramine comprises a single Nitrogen atom and a set of Chlorine atoms. These valence electrons are used as building blocks in the Lewis structure.
#Molecular geometry table with bond angles free
Thus, valence electrons break free to participate in the chemical bond formation or electron exchange.Įach atom in the molecule contributes a set number of valence electrons depending upon their atomic number and position on the periodic table. Here, the force of attraction from the nucleus on these electrons is weak. Valence electrons are those electrons that lie in the outermost shell of the atom. Dots and lines are used in the Lewis structure to describe electrons and chemical bonds, respectively.įirst, the number of valence electrons present in the structure must be determined.

They’re usually the first figures drawn to represent molecules and understand their properties. Lewis dot structures are schematic representations of valence electrons and bonds in a molecule. CONCLUDING REMARKS NCl 3 Lewis Structure.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
